Education Redefined: A Guide to the New Education Policy 2023 in India
NEP2023 is a paradigm shift in the Indian education landscape. The New National Education Policy, implemented in 2023, marks a significant milestone in India’s education system. After following the same norms for 34 years, the Ministry of Education (formerly known as MHRD) introduced significant changes on July 29, 2020. With the adoption of the New National Education Policy in 2023, educators and students may naturally wonder what it truly entails.
In this blog, we aim to provide answers by examining the major features of the policy and delving into the NEP’s V+III+III+IV structure.
So without further ado, let’s begin.
National Education Policy (NEP) – An Overview
Organized by the Ministry of Education, India, NEP was launched on 29th July 2020. With the motto “Educate, Encourage and Enlighten”, it is bringing new amendments to modernize and improve the existing education system of India. It aims to accomplish 100% youth and adult literacy with four powerful pillars – Access, Equity, Quality, and Accountability.
The Main Goals of National Education Policy 2023
The primary objective of the National Education Policy is to elevate the standard of education in India to an international level, positioning the country as a leader in knowledge-based sectors. This is achieved through the policy’s focus on universalizing education.
Key Tenets of the New Education Policy:
- Unlocking the true potential of each learner
- Enhancing reading and numeracy skills
- Providing flexible learning opportunities
- Investing in public education
- Enhancing the quality of education
- Empowering learners by promoting research and good governance
- Ensuring transparency in education policy
- Emphasizing the use of digital assessment platforms
- Integrating digital tools and blended learning pedagogies
- Promoting multilingual education
- Enhancing creativity and logical thinking skills
Now what are the major reforms brought by the NEP 2023? Let’s find out.
Transformative Reforms in the New Education Policy 2023
- V+III+III+IV model: Replacing the X+II structure with a new model that spans 5 years of foundational education, followed by 3 years of preparatory education, 3 years of middle education, and 4 years of secondary education.
- Integration of disciplines: No distinct divisions between arts, sciences, academic, vocational, curricular, and extracurricular subjects.
- Focus on foundational skills: Prioritizing foundational reading and numeracy skills.
- Language flexibility: No imposition of any state language on students studying in different states.
- Board Examinations: Allowing students to take board exams twice.
- Increased education investment: Increasing the government’s expenditure on education from 1.7% to 6% of the country’s GDP.
- Gender inclusion fund: Establishing a dedicated fund for promoting gender inclusion in education.
- Special attention to gifted children: Ensuring suitable education for gifted students.
- Four-year undergraduate courses: Extending the duration of undergraduate programs to four years.
- B.Ed Course requirement: Requiring a four-year integrated B.Ed course for teacher positions.
- Common Admission Examination: Implementing a common entrance examination for admission to Higher Education Institutions (HEIs).
- Phasing out the M.Phil program: Gradual elimination of the Master of Philosophy program from the education system.
- Diverse secondary school options: Offering a range of disciplines in secondary schools, including arts and crafts, vocational courses, and physical education.
- PARAKH organization: Establishing the PARAKH organization to set standards for board examinations.
- Inclusion of Indian literature: Making Indian literature and classical languages part of the educational curriculum.
- Reduced exams: Conduct exams only in classes 2nd, 5th, and 8th instead of every academic year.
What is the New V+III+III+IV Education Structure?
NEP 2023 introduces a significant change in the education system by replacing the long-standing X+II structure with the innovative V+III+III+IV structure.
Under the new Pedagogical and Circular Structure, the government has divided students’ schooling into four distinct stages: Secondary, Middle, Preparatory, and Foundational. Each of these stages plays a crucial role in the educational development of students throughout their school years. Here is a breakdown of how these four stages will be organized within the schooling system:
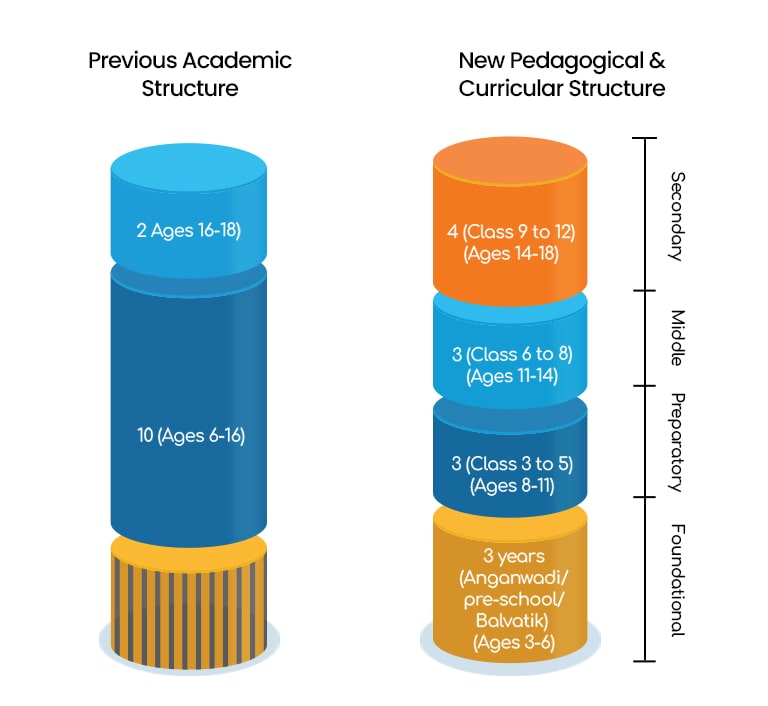
- Foundational stage (5): This initial stage will focus on nurturing young minds from ages 3 to 8, emphasizing a play-based and activity-oriented approach to education in pre-school and 1st-2nd grade.
- Preparatory stage (3): From ages 8 to 11, this stage aims to build a strong foundation in various subjects and foster critical thinking skills in 3rd-5th grade.
- Middle stage (3): Spanning ages 11 to 14, this stage aims to provide a comprehensive education that includes a wide range of subjects and encourages experiential learning in 6th-8th grade.
- Secondary stage (4): From ages 14 to 18, this stage will focus on subject specialization and preparation for higher education or vocational training in 9th-12th grade.
This revamped structure aims to provide a more holistic and well-rounded education, catering to the different developmental needs of students at various stages.
Importance of the V+III+III+IV Structure in NEP 2023
The implementation of the V+III+III+IV structure in the new education policy holds significant value as it prioritizes the cognitive development stage of students.
This revised structure provides a more detailed framework for the various stages of students’ schooling, ensuring their overall growth and progress. Unlike the previous X+II structure, the V+III+III+IV model strengthens the educational foundation of students from the foundational stage all the way to the secondary stage.
The new structure also facilitates the effective utilization of the Right to Education, as it now encompasses ages 3 to 18 instead of the previous 6 to 14 age range. Consequently, students will receive support right from the beginning of their educational journey.
Moreover, the introduction of the V+III+III+IV structure is expected to significantly improve student retention rates. With this new structure in place, more students are likely to remain in the same school throughout their academic journey.
Ultimately, a higher literacy rate resulting from the implementation of this structure will contribute to the overall advancement of our country’s future.
Furthermore, NEP 2023 emphasizes the significance of integrating digital tools and platforms into the education system. Let’s dive in.
Digital Inclusions in the National Education Policy 2023
In line with technological advancements, digital teaching methods have emerged as an integral part of modern education. Let’s explore the government’s digital initiatives outlined in the NEP 2023 to enhance the quality of education:
- The government will establish the National Educational Technology Forum (NETF) to promote and enhance the implementation of digital teaching methods in schools. This forum will serve as a platform for sharing innovative ideas and strategies related to digital education across different educational institutions.
- To further bolster digital education resources, a new unit will be introduced that will operate nationwide. This unit will focus on developing and curating digital learning materials, tools, and resources to support teachers and students in their educational journey.
- Furthermore, NEP 2023 emphasizes the integration of technology in classrooms to streamline and enhance various educational processes. This integration aims to leverage technology for instructional delivery, assessment methods, and overall classroom management, providing students with a more engaging and interactive learning environment.
Through these digital inclusions, the government aims to leverage technology to improve the overall quality of education and ensure students have access to diverse digital resources and innovative teaching methodologies.
Now that we’ve discussed the significance of digital education in NEP 2023, let’s explore how it can be implemented.
Role of Möbius in the National Education Policy 2023
DigitalEd India aims to transform STEM education through a digital learning ecosystem.
DigitalEd offers the interactive Möbius platform, a cutting-edge digital learning platform that has garnered global recognition. With its seamless interface and interactive features, Möbius fuels curiosity, bridges knowledge gaps, and ensures a consistent and engaging learning experience.
Here’s how Möbius facilitates the digital inclusions of the NEP 2023:
- Design, develop and deploy digital courses and content repositories to make them easily accessible online and on demand.
- Collaborate with other educators and students to share ideas, improve course content and explore different teaching methodologies.
- Modernize education and increase knowledge by integrating powerful multimedia visualizations into the course content.
- Foster a blended learning environment with an intuitive and interactive digital platform, instilling consistency and continuity between classroom learning and outside-the-class learning.
- Evaluate the students on a digital assessment platform, leveraging multiple pathways like in-line questions, algorithmically randomized questions, adaptive questions, digital quizzes, etc.
- Enhance connectivity between students and educators to strengthen learning by facilitating valuable and timely feedback whenever needed.
- …and more
Want to explore the Möbius experience? Book a demo today!
Embark on an exciting educational journey with Möbius as your digital guide!
One Reply to “Education Redefined: A Guide to the New Education Policy 2023 in India”
latest status of implementation of NEP2020 in India requested