Leading the way in digital education, with Education 4.0
The employment landscape in the 21st century requires educators to provide experiential learning that enables the students to handle situations in the real world and be at par with the technologically evolving industries.
The education industry has been experiencing a technological metamorphosis for more than a decade now, and yet many educational institutions lack basic digital tools or means of connectivity.
The types of educational institutions can be bifurcated into 3 categories:
• Achievers: Equipped with devices, digital platforms, and connectivity.
• Challengers: Equipped with either devices, digital platforms, or connectivity.
• Aspirers: Lacking devices, digital platforms, and connectivity.
Here’s an infographic to explain the educational disparities in India:
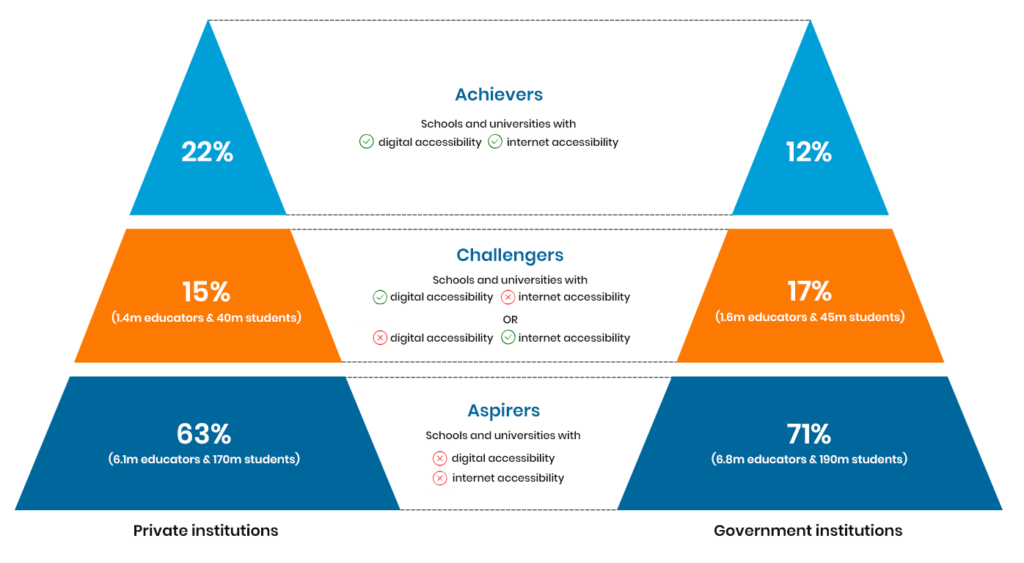
It is evident that an alarming number of private and government schools and other educational institutions are yet to integrate devices and connectivity into their curriculum.
This is where the education 4.0 initiative comes into play.
What is Education 4.0?
The COVID-19 pandemic shone a light on the education sector’s long-standing problems in India. It made learning gaps wider for both students and teachers, which made it harder to build a society where everyone can easily access high-quality education.
The Education 4.0 India initiative was developed by the World Economic Forum and UNICEF in May 2020 to address inequalities in the Indian education system and to empower India’s youth to become the innovators and changemakers of the next generation.
The organizations have joined forces as part of Education 4.0 in India with the goal of bolstering the government’s initiatives in the fields of education, skill development, and employment as well as implementing solutions at a large scale.
Education 4.0 initiative launched the KINDLE (Knowledge & Information Network for Digital Learning & Education) approach to bridge learning gaps, facilitate skill development for 21st-century jobs, and make education more widely accessible by utilizing digital learning and other technologies.
The KINDLE approach addresses the following key themes to enrich higher education in India:
- School-To-Work (S2W) Transition
- Connecting the Unconnected
Let’s discuss this in detail.
School-To-Work Transition
With the introduction of new technologies, a greater emphasis on specialization, and accelerating globalization, the employment landscape is rapidly evolving on a global scale. India has one of the youngest populations in the world, with a median age of only 28 years. This demographic bulge is anticipated to last until 2055.
The school-to-work transition is focused on a person’s ability to find a path that aligns with their interests and develop the skills needed to deal with evolving industries, technological advancements, and labor market conditions.
Steps that can be taken to facilitate a seamless school-to-work transition:
• Offer opportunities for internships, volunteering, and apprenticeships that will expose students to various career options.
• Technology can be integrated and used in ways to deliver experiential learning for a more practical approach towards education.
• Immersive technologies can be used to reinforce concepts and make complex concepts (quantum physics, chemical reactions, etc.) easier to comprehend.
• Introduce digital platforms to reinforce lessons, increase knowledge retention, and prepare them for digitally advanced industries.
• Train teachers on digital platforms to enhance online learning experiences and establish a mentorship network online to optimize teaching strategies.
• Adopt blended strategies that allow for a seamless transition between physical classrooms and digital platforms.
• Enable safe training for real-world scenarios through experiential learning with the help of Augmented and Virtual Reality technologies.
Connecting the Unconnected
To maintain learning continuity during the pandemic-related school and university closures, administrators and educators across the nation adopted a variety of digital learning solutions. But in order to reach every learner and connect those who aren’t already using the internet, other digital technologies, or related devices, a suitable plan of action is needed.
Content needs to be localized, accessible through multiple touchpoints, and compatible with a variety of devices. It is crucial to connect universities, people, and communities with such solutions in order to improve learning, decrease access disparities, and address the learning divide.
4 factors are essential to cultivate an interconnected learning ecosystem:
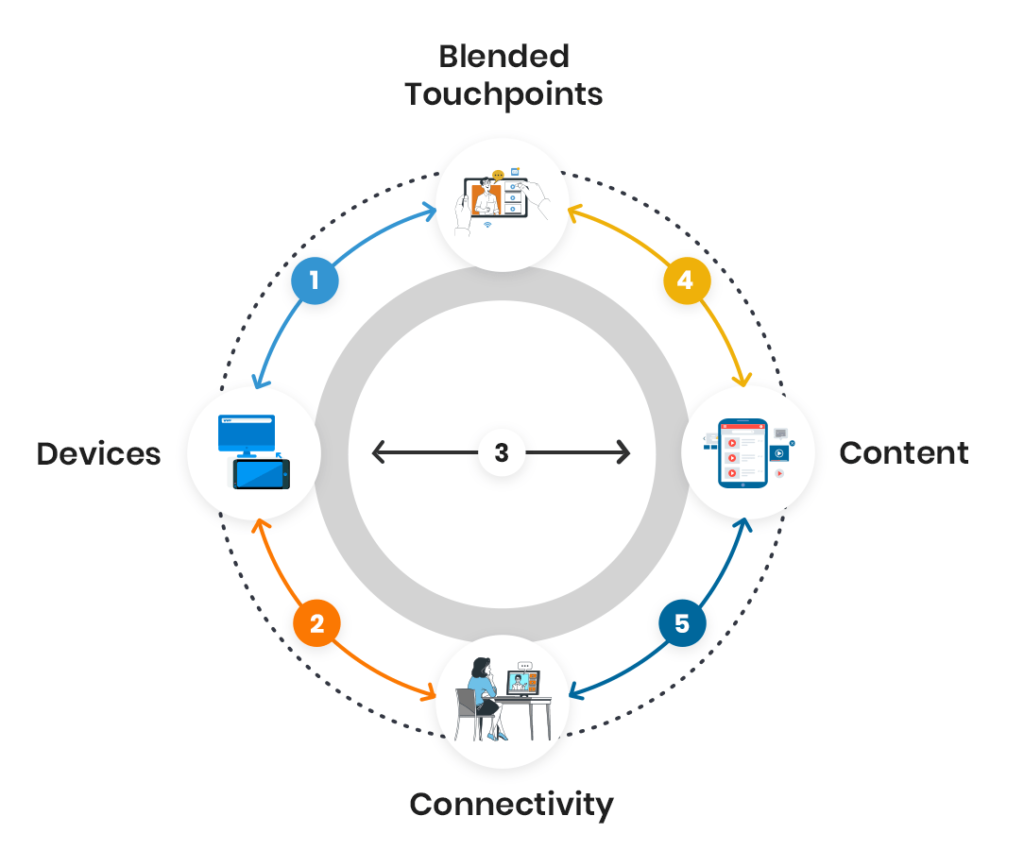
- Possibilities and opportunities for e-content creation:
• Design and development of context-specific digital content repositories for various courses.
• Digital learning platforms where educators can create and distribute completely bespoke course content, catering to the specific needs of the students and their curriculum.
• Utilizing cutting-edge content to improve the learning experience using innovative technologies like simulation, AI, and AR/VR.
• Including multimedia content, interactive elements, quizzes, mock tests, and inline questions in-between lessons to spark curiosity among students.
- Possibilities and opportunities for blended touchpoints:
• Utilizing and scaling technological solutions like smart devices and digital platforms.
• Leveraging technology to create a blended learning environment for eliminating learning gaps.
• Leveraging analytics for a data-driven approach to make well-informed decisions and strategize innovative teaching techniques.
• Utilizing advanced technology like artificial intelligence and machine learning to deliver personalized learning experiences.
- Possibilities and opportunities for increasing access to devices:
• Evolve teaching/learning methods by utilizing seamless user interfaces with cutting-edge features.
• Cohesive digital learning platforms where educators and students can collaborate from across the globe.
• Fostering a learning environment that blends technology with traditional classrooms to yield the best results.
• Ensuring that the digital content and the devices are interoperable.
- Possibilities and opportunities for increasing connectivity:
• Leveraging digital technologies to help educators stay connected with the students throughout the learning process.
• Offering ways to get instant feedback to close knowledge gaps and eliminate confusion in complex concepts.
• Technological solutions like digital platforms, content repositories, and chatrooms to keep educational institutions connected.
• Delivering content that is compatible across sources, platforms, and different bandwidths.
Now that we’ve discussed the goals and opportunities of the Education 4.0 India Initiative, let’s talk about its implementation.
Implementing Education 4.0 Initiative with DigitalEd India
DigitalEd India is a joint venture of DigitalEd, Canada, and Binary Semantics Limited, India. It is an EdTech company that takes STEM learning/teaching experiences a step further through a comprehensive digital learning ecosystem.
Möbius, a product of DigitalEd, is a seamless and interactive e-learning platform that is used all over the world to design, develop and distribute online STEM courses. It helps spark curiosity, bridge learning gaps, and maintain consistency in the learning process with an effective blended learning pedagogy.
The Möbius platform facilitates the Education 4.0 initiative in the following ways:
• Eliminate the illusion of knowing with a dynamic platform, instilling continuity and consistency in the learning experiences.
• Develop and deploy extensive STEM content repositories to make them easily accessible online and on demand.
• Maximize connectivity between students and educators to reinforce knowledge with valuable and immediate feedback whenever necessary.
• Choose from 15 types of in-line questions (for instance, list questions, sorting questions, HTML questions, multiple choice questions, sketch questions, etc.) to analyze students’ progress, allowing educators to deliver personalized learning experiences.
• Integrate interactive multimedia content in-between lessons to maximize knowledge retention.
• Educators can break down challenging tasks into smaller tasks to make the teaching process more streamlined and manageable;
• Transform short-term memory into long-term knowledge through repeated self-evaluation with algorithmically randomized questions.
And more.
Want to explore the Möbius experience?
Contact us to book a product demo.
And stay tuned for more additions to the Education 4.0 series.